JUSTICE HAS BEEN SERVED
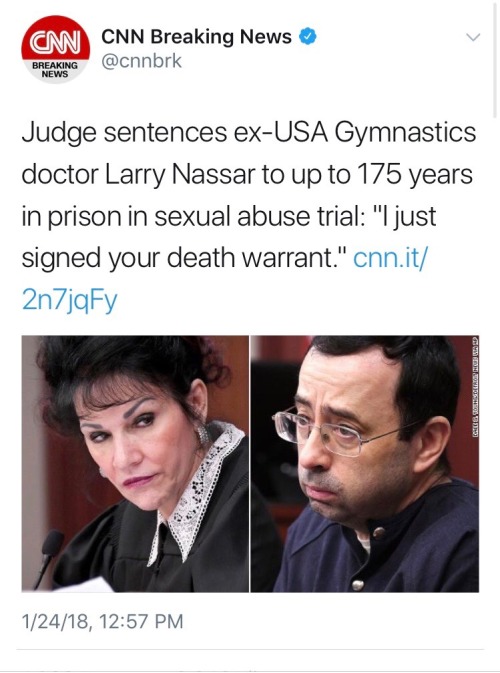

JUSTICE HAS BEEN SERVED
-
 fishtacofriday reblogged this · 1 year ago
fishtacofriday reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 fishtacofriday liked this · 1 year ago
fishtacofriday liked this · 1 year ago -
 gallifreyansunsets reblogged this · 1 year ago
gallifreyansunsets reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 dystopian-trainer liked this · 1 year ago
dystopian-trainer liked this · 1 year ago -
 maponawall137 liked this · 1 year ago
maponawall137 liked this · 1 year ago -
 returnofthedarknight liked this · 1 year ago
returnofthedarknight liked this · 1 year ago -
 bellyfairy liked this · 1 year ago
bellyfairy liked this · 1 year ago -
 kaosafro reblogged this · 1 year ago
kaosafro reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 slimmepink liked this · 1 year ago
slimmepink liked this · 1 year ago -
 agentdaedalus reblogged this · 1 year ago
agentdaedalus reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 lilith-the-sinful reblogged this · 1 year ago
lilith-the-sinful reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 madvillaingt8 reblogged this · 1 year ago
madvillaingt8 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 echoesinajar liked this · 1 year ago
echoesinajar liked this · 1 year ago -
 echoesinajar reblogged this · 1 year ago
echoesinajar reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 blvckstvr777 reblogged this · 1 year ago
blvckstvr777 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 blvckstvr777 liked this · 1 year ago
blvckstvr777 liked this · 1 year ago -
 honorarypossum liked this · 1 year ago
honorarypossum liked this · 1 year ago -
 ladybugsumbrellas reblogged this · 1 year ago
ladybugsumbrellas reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 ladybugsumbrellas liked this · 1 year ago
ladybugsumbrellas liked this · 1 year ago -
 skele-squirrel liked this · 1 year ago
skele-squirrel liked this · 1 year ago -
 qaz1234etu liked this · 1 year ago
qaz1234etu liked this · 1 year ago -
 aloeverawrites liked this · 1 year ago
aloeverawrites liked this · 1 year ago -
 sweosaurpainter869 liked this · 1 year ago
sweosaurpainter869 liked this · 1 year ago -
 nuthtwombat900 liked this · 1 year ago
nuthtwombat900 liked this · 1 year ago -
 kajuwu reblogged this · 1 year ago
kajuwu reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 quirkyrahne28 liked this · 1 year ago
quirkyrahne28 liked this · 1 year ago -
 trippy-xylophone reblogged this · 1 year ago
trippy-xylophone reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 itsthatbeech liked this · 1 year ago
itsthatbeech liked this · 1 year ago -
 ratsconfusion liked this · 1 year ago
ratsconfusion liked this · 1 year ago -
 kannoaya liked this · 1 year ago
kannoaya liked this · 1 year ago -
 letskeepshady liked this · 1 year ago
letskeepshady liked this · 1 year ago -
 marca-espana liked this · 1 year ago
marca-espana liked this · 1 year ago -
 deamn liked this · 1 year ago
deamn liked this · 1 year ago -
 iamsmaug reblogged this · 1 year ago
iamsmaug reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 happytohavebeenfound reblogged this · 1 year ago
happytohavebeenfound reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 lesonicaro reblogged this · 1 year ago
lesonicaro reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 foxbodymustangs liked this · 1 year ago
foxbodymustangs liked this · 1 year ago -
 goldlipstick liked this · 1 year ago
goldlipstick liked this · 1 year ago -
 megakimathi liked this · 1 year ago
megakimathi liked this · 1 year ago -
 christmas-connections liked this · 1 year ago
christmas-connections liked this · 1 year ago -
 dehaannews liked this · 1 year ago
dehaannews liked this · 1 year ago -
 magnetoxo liked this · 1 year ago
magnetoxo liked this · 1 year ago -
 biciudades liked this · 1 year ago
biciudades liked this · 1 year ago
More Posts from Jorgefg89







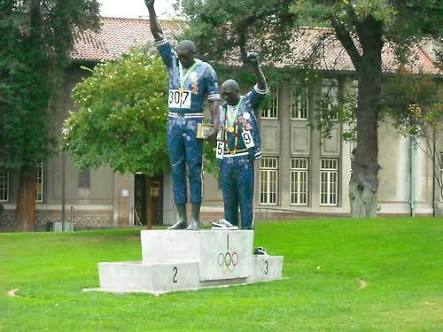

We should be more pro-active or we’ll see more of such sad fates of honest people.
Pharmacokinetics Overview
(Absorption and distribution of drugs)
The study of the time course of drugs and their metabolites in the body (what the body does to the drug) consisting of:
administration
absorption
distribution
metabolism
excretion
Administration
Enteral (passes through intestine)
oral (mouth)
buccal/sublingual (applied in cheek/under tongue)
Gastrosomy (surgical opening through the abdomen into the stomach)
Topical (applied directly)
Nasal
Rectal
Ophthalmic (eyes)
Parentral (injection)
Intravenous (into veins)
intramuscular (into muscles)
intradermal (within layers of skin)
subcutaneous (under the skin)
Drug molecules move around the body either through bulk flow (bloodstream, lymphatics or cerebrospinal fluid) or diffusion (molecule by molecule over short distances)

Absorption
Passage of drug from its site of administration into plasma - important for all routes except intravenous injection.
Injection
IV = fastest route of administration
bolus injection = very high concentration of drug
rate limiting factors = diffusion through tissues and removal by local blood flow
Drugs need to pass through membranes (cell membranes, epithelial barriers, vascular endothelium, blood-brain barrier, placenta barrier etc) via
passive diffusion through lipids
carrier-mediated
passage through membrane pores/ion channels
pinocytosis (ingestion into a cell by the budding of small vesicles from the cell membrane)
Diffusion through lipid
non-polar molecules can dissolve freely in membrane lipids
the rate is determined by the permeability coefficient (P)(solubility in the membrane and diffusibility) and the concentration difference across the membrane
pH and Ionisation
Many drugs are weak acids or weak bases
exist in unionised or ionised forms
pH = balance between the two forms
ionised forms have low lipid solubility
uncharged however the drug is usually lipid soluble

ionisation affects:
rate of drug permeation through membranes
steady state distribution of drug molecules between aqueous compartments if pH difference exists between them
Therefore:
urinary acidification accelerates the excretion of weak bases and slows that of weak acids
alkalisation has opposite effect
increasing plasma pH causes weak acids to be extracted from CNS into plasma
Reducing plasma pH causes weakly acidic drugs to become concentrated in CNS, increasing neurotoxicity
Bioavailibility
Bioavailibility (F) indicates the fraction of an orally administered dose that reaches systemic circulation intact, taking into account both absorption and local metabolic degradation
determined by comparison between oral and IV absorption

affected by:
drug preparation
variation in enzyme activity of gut
gastric pH
intestinal motility
Volume of Distribution
Vd is defined as the volume of fluid required to contain the total amount, Q, of drug in the body at the same concentration as that present in the plasma, Cp
determined by relative strength of binding between drug and tissue compared with drug and plasma proteins
tight binding to tissue but not plasma –> drug appears to be dissolved in large volume –> large Vd (eg chloropromazine)
tight binding to plasma –> V can be very close to blood volume –> low Vd (eg warfarin)


PHARMACOKINETICS CALCULATIONS
Single-Dose: •Vd = Dose/Co •t1/2 = 0.7 x Vd/Cl
Multiple-Dose, Infusions: •Ko = Cl x Css •LD = Vd x Cp/f •MD = Cl x Css x dosing interval/f
Vd: volume of distribution Co: plasma [ ] at zero time Cp: plasma [ ] t1/2: half life Cl: clearance = free fraction x GFR Ko: infusion rate Css: steady state [ ] LD: loading dose MD: maintaining dose f: bioavailability







